Green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources
such as wind, solar, or hydroelectric power, to power water electrolysis. The electrolysis process involves splitting water molecules (H2O) into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) without generating carbon emissions. This method contrasts with traditional hydrogen production, such as steam methane reforming, which relies on fossil fuels and creates greenhouse gas emissions.
The green hydrogen market in India is expected to be worth $30-35 billion by 2035-2040 (assuming optimistic demand). In India, the green hydrogen market (sales) is expected to reach $10 billion by 2030 and $35 billion by 2040 (per annum estimates). Major industries like transportation and industrial production rely heavily on imported fossil fuels. Today, hydrogen is required for a variety of reasons. Green hydrogen production using renewable energy can be critical in low-carbon and self-sufficient economic routes.
The use of Green Hydrogen and its derivatives, the machinery and technology used, and the infrastructure development associated with it in many new programs in the country, such as green fuel, green energy, green mobility, green farming, green buildings and equipment, and policies for efficient use of this energy source in various economic sectors, will mean that the industry is bound to see exponential growth in the demand for Green Hydrogen and its derivatives, the machinery and technology used, and the infrastructure development associated with it.
The critical steps in green hydrogen production
- Electrolysis: Renewable electricity (from sources like solar or wind power) powers an electrolyzer, which splits water into hydrogen and oxygen. The process separates hydrogen from water, generating ‘green’ hydrogen without producing greenhouse gases or other harmful emissions.
- Renewable Energy Sources: The renewable energy sources used for electrolysis are crucial in making the overall process environmentally friendly. The entire hydrogen production cycle becomes sustainable and emission-free by utilizing solar, wind, or hydroelectric power. Green hydrogen holds immense promise as a clean, sustainable energy carrier. It can be used in various sectors and industries, including transportation, power generation, industrial processes, and energy storage. The widespread adoption of green hydrogen is integral to reducing carbon emissions and mitigating climate change by providing a versatile and low-carbon energy source.
Green Hydrogen Manufacturing
Green hydrogen manufacturing involves the production of hydrogen through an environmentally sustainable process using renewable energy sources. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Electrolysis : Electrolysis is the core process used to produce green hydrogen. Water (H2O) is separated into its components—hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2)—through the application of an electric current. This occurs within an electrolyzer, a device that contains an anode and a cathode separated by an electrolyte.
- Renewable Energy Input : The electricity used in electrolysis comes from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydroelectric power. These sources ensure that the overall hydrogen production cycle is environmentally friendly and does not generate carbon emissions.
- Types of Electrolysis : Different electrolyzers are used for hydrogen production, including alkaline electrolyzers, polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) electrolyzers, and solid oxide electrolyzers. Each type has its advantages regarding efficiency, scalability, and operating conditions.
- Scaling Up Production : Green hydrogen manufacturing involves installing electrolysis plants to scale production to meet demand. These plants may range from small-scale installations to extensive industrial facilities.
- Storage and Distribution : Once produced, green hydrogen needs to be stored and distributed. Storage methods can include compressed gas, liquefaction, or conversion into other forms, such as ammonia, for more accessible transport. Infrastructure for transporting and utilizing hydrogen as an energy carrier must also be developed.
Challenges in Green Hydrogen Manufacturing
- Cost: One of the primary challenges is the cost of production. Currently, green hydrogen is more expensive than hydrogen generated from fossil fuel-based processes.
- Efficiency: Improving the efficiency of electrolysis processes and reducing energy losses is crucial to make green hydrogen more cost-effective.
- Infrastructure: Developing infrastructure for large-scale hydrogen production, storage, and distribution is essential for widespread adoption.
- Technological Advancements: Research and development are ongoing to improve the performance and reduce the costs of electrolyzers and associated technologies.
The future of green hydrogen manufacturing in India and worldwide largely depends on technological advancements, reduced production costs, supportive government policies, and collaborative efforts among various stakeholders to drive sustainable and efficient production processes. As technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, green hydrogen manufacturing is poised to be pivotal in transitioning towards a more sustainable, low-carbon energy future.
Green Hydrogen in Indian Industrial Use
- Steel Production – The steel industry is a significant consumer of hydrogen. Green hydrogen can significantly reduce carbon emissions when used as a reducing agent in steel manufacturing. Indian steel companies are exploring hydrogen as a cleaner alternative to traditional processes like coking coal in blast furnaces.
- Chemical Manufacturing – Industries involved in chemical production are examining green hydrogen as a feedstock. Hydrogen is a crucial component in the synthesis of various chemicals. These industries can reduce their carbon footprint and environmental impact by using green hydrogen.
- Refining and Petrochemicals – Refineries and petrochemical plants can potentially integrate green hydrogen into their processes, replacing hydrogen produced from fossil fuels. This shift can lower the carbon intensity of their operations.
- Transportation – Indian industries are also exploring using hydrogen fuel cells in transportation, especially for commercial vehicles. Hydrogen fuel cells can power buses and trucks, offering a zero-emission alternative to conventional diesel-powered vehicles.
- Power Generation – Green hydrogen can be used in power generation. Some industries consider hydrogen a storage solution for renewable energy sources, allowing for a more consistent power supply even when solar or wind energy generation is intermittent.
- Ammonia Production – Green hydrogen can produce ammonia, an essential component in fertilizers. This shift can contribute to sustainable and eco-friendly agriculture practices in India.
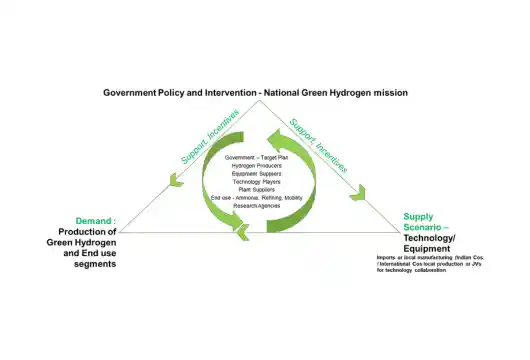
National Green Hydrogen Mission
Green hydrogen can be created from biomass by thermochemical and biological processes and by electrolyzing water with renewable energy. The nation currently produces relatively little hydrogen from renewable resources. Several organizations have declared their intentions to establish Green Hydrogen/Green ammonia-producing facilities in India. These are still in the early stages, though. The two main expenses of producing green hydrogen are those related to electrolyzers and renewable energy input. The total cost of delivered green hydrogen for any given application would include capital expenses, water supply and purification, distribution and storage, conversion of hydrogen to appropriate derivatives, and supporting infrastructure.
Components of the Green Hydrogen Mission:
- We are facilitating demand creation through exports and domestic utilization.
- Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) program domestic manufacturing of electrolyselectrolyzersction of Green Hydrogen.
- Development of Green Hydrogen Hubs
- Support for infrastructure developments
- Establishing a robust framework of regulations and standards
- Research & Development program
- Skill development program
- Public awareness and outreach program
Future of Green Hydrogen in India
- Government Initiatives : The Indian government has shown a keen interest in promoting green hydrogen. The proposed National Hydrogen Energy Mission aims to provide a roadmap for scaling up hydrogen production and usage across various sectors, signifying a dedicated commitment to advancing the technology.
- Integration with Renewable Energy : India’s vast potential for solar and wind energy provides a significant advantage in harnessing these renewable sources to power electrolysis for green hydrogen production. As the costs of renewable energy continue to decline, it will further enhance the attractiveness of green hydrogen.
- Technological Advancements : Ongoing research and development efforts in India and globally are focused on enhancing electrolysis technologies, reducing costs, and improving the efficiency of green hydrogen production methods. Advancements in electrolyzer technology are crucial for making green hydrogen more competitive in the energy market.
- Sectoral Integration : Industries such as steel, chemicals, transportation, and power generation are likely to adopt green hydrogen increasingly. The shift toward low-carbon and zero-emission practices aligns with global sustainability goals.
- Investment and Partnerships : There’s growing interest and investment in green hydrogen production. Partnerships between the government, private sectors, and international collaborations are being forged to expedite the development and adoption of green hydrogen technologies.
- Infrastructure Development : Establishing hydrogen refueling stations, storage facilities, and an integrated hydrogen supply chain will be crucial for widely adopting green hydrogen.
Promotion of Green Hydrogen in India
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) : MNRE is a crucial government agency responsible for developing and promoting renewable energy in India. It plays a vital role in shaping policies and schemes related to green hydrogen.
- National Hydrogen Energy Mission : The National Hydrogen Energy Mission is a significant initiative by the Government of India to promote green hydrogen. It provides a comprehensive framework for the development and utilization of hydrogen.
- Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA) : IREDA is a financial institution that supports renewable energy projects and plays a role in financing green hydrogen initiatives.
- NITI Aayog : NITI Aayog is involved in policy formulation and strategic planning. It has been actively working on recommendations and strategies to promote green hydrogen as a sustainable energy solution.
- Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) : IOC has announced plans for a Hydrogen Energy Mission focusing on green hydrogen production, storage, and utilization. The corporation’s initiatives could contribute significantly to the growth of India’s green hydrogen sector.
- Power Finance Corporation (PFC) and Rural Electrification Corporation (REC) : These financial institutions have historically supported renewable energy projects and could extend their support to green hydrogen initiatives.
- International Solar Alliance (ISA) : ISA, a treaty-based intergovernmental organization, focuses on promoting solar energy. As solar power is often involved in green hydrogen production, ISA’s efforts indirectly contribute to the growth of green hydrogen in India.
- Hydrogen Energy and Fuel Cells Programme by MNRE : MNRE has been involved in developing a Hydrogen Energy and Fuel Cells Programme, which includes research, development, and demonstration projects related to hydrogen and fuel cells.
- The Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT program) : This resembles a Production-linked Incentive scheme for the green hydrogen sector. It offers fiscal benefits for three and five years for producing Green Hydrogen and the manufacturing of Electrolysers, respectively.
 Author: Anamika Mani (Assistant Marketing Manager) Company Details – BDB India Private Limited – Market Research and Business Consulting.Website – https://bdbipl.com/
Author: Anamika Mani (Assistant Marketing Manager) Company Details – BDB India Private Limited – Market Research and Business Consulting.Website – https://bdbipl.com/